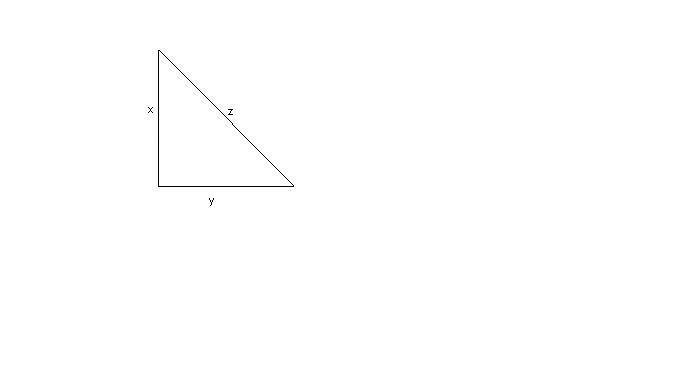Determina la lunghezza dei cateti di un
triangolo rettangolo sapendo che la somma delle lo lunghezzeè
[math]21cm[/math]
e che l'ipotenusa misura
[math]15cm[/math]
.
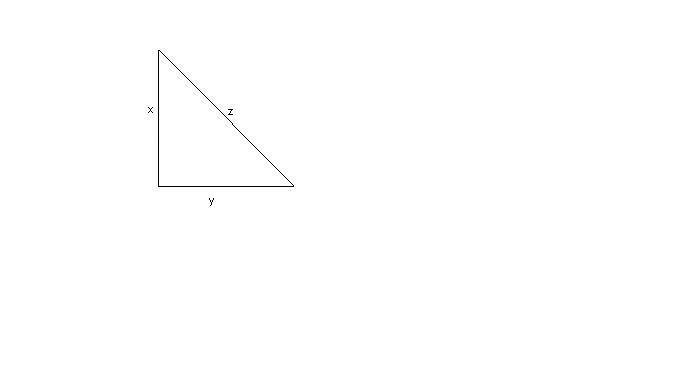
Svolgimento
Indichiamo con
[math]x[/math]
e
[math]y[/math]
i due cateti e con
[math]z[/math]
l'ipotenusa, i dati sono:
[math]x+y=21cm \wedge z=15cm[/math]
Per il teorema di Pitagora sappiamo che
[math]z=\sqrt{x^2+y^2} \Rightarrow \sqrt{x^2+y^2}=15cm[/math]
.
Mettiamo a sistema le due equazioni e procediamo nella risoluzione
[math]\begin{cases} \sqrt{x^2+y^2}=15 \\ x+y=21 \end{cases}[/math]
;
[math]\begin{cases} \sqrt{x^2+y^2}=15 \\ x=21-y \end{cases}[/math]
;
Eleviamo al quadrato ambo i membri della prima equazione e procediamo per sostituzione
[math]\begin{cases} x^2+y^2=225 \\ x=21-y \end{cases}[/math]
;
[math]\begin{cases} (21-y)^2+y^2=225 \\ x=21-y \end{cases}[/math]
;
[math]\begin{cases} 441-42y+y^2+y^2=225 \\ x=21-y \end{cases}[/math]
;
Semplificando
[math]\begin{cases} 2y^2-42y+216=0 \\ x=21-y \end{cases}[/math]
;
Dividendo la prima equazione per
[math]2[/math]
si ha:
[math]\begin{cases} y^2-21y+108=0 \\ x=21-y \end{cases}[/math]
;
Risolviamo l'equazione di secondo grado
[math]y^2-21y+108=0[/math]
[math]\Delta=b^2-4ac=(-21)^2-(4 \cdot (108) \cdot 1)=441-432=9[/math]
[math]y_(1,2)=\frac{-b \pm \sqrt{\Delta}}{a}
[math]\frac{21 \pm \sqrt{9}}{2}=\frac{21 \pm 3}{2 \Rightarrow y_1=9 \lor y_2}=12[/math]
.
Pertanto
[math]\begin{cases} y_1=9 \\ x_1=21-y_1 \end{cases} \Rightarrow \{(y_1=9),(x_1=12)\}[/math]
;
[math]\{(y_2=12),(x_2=21-y_2)\} \Rightarrow \begin{cases} y_2=12 \\ x_2=9 \end{cases}[/math]
.
Quindi se scegliamo come cateto minore
[math]x[/math]
e come cateto maggiore
[math]y[/math]
, questi misurano rispettivamente
[math]9cm[/math]
e
[math]12cm[/math]
; altrimenti viceversa.